Artificial intelligence (AI) software developer Lunit is directing attention to recent research highlighting the benefits of its chest x-ray AI software for detecting lung cancer.
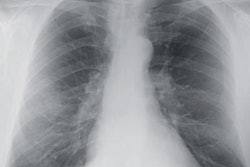
In a study conducted by a joint research team from Lunit and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), the company's Insight CXR AI software yielded 94% sensitivity and 83% specificity for detecting malignant lung nodules in 5,485 chest radiographs from the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST).
What's more, the algorithm also provided higher sensitivity than the radiologists in the NLST study, showing the software's potential to help detect lung cancer when used as a second reader, according to the vendor. The research was published online September 24 in JAMA Network Open.
As detecting lung cancer on chest radiographs is challenging for radiologists due to the modality's projectional nature, low-dose CT is currently recommended for lung cancer screening, noted senior author Dr. Subba Digumarthy of MGH. However, CT is also less accessible and more expensive than chest radiography, and it exposes patients to more radiation.
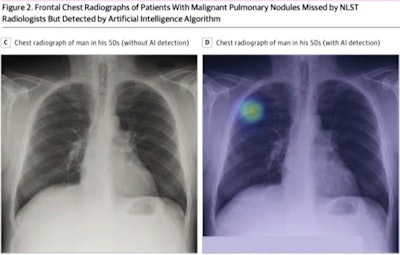 Image courtesy of Lunit.
Image courtesy of Lunit."This study shows that AI can provide diagnostic value to more patients by supplementing the shortcomings and maintaining the advantages of x-ray diagnosis," said Digumarthy in a statement from Lunit.