An AI method for measuring prostate tumor volume based on multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) data shows promise for predicting treatment outcomes, researchers have reported.
"[We found that the] volume of AI-segmented intraprostatic tumors was an independent prognostic factor for outcomes of localized prostate cancer treated with radical prostatectomy and radiation therapy," wrote a group led by David Yang, MD, of Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston.
Multiparametric MRI has "revolutionized the management of localized prostate cancer," the team explained, noting that MRI characteristics of prostate tumors such as PI-RADS scores and lesion size have been associated with negative treatment outcomes. But these characteristics can be influenced by interobserver variability, and using AI tumor segmentation algorithms with MRI data shows promise for improving consistency.
The researchers explored whether the total volume of prostate tumors (which they dubbed VAI) as measured by AI-generated segmentations could predict treatment response in patients with localized prostate cancer who underwent radiation therapy or radical prostatectomy. They conducted a study that included 732 patients with prostate cancer who had an MRI exam and were treated with radiation therapy or radical prostatectomy between January 2021 and August 2023.
The group used an AI segmentation algorithm (ThennU-Net v.1.0) trained with the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS); it calculated areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUCs) for total volume of VAI and National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) risk categorization for the prediction of five-year metastasis (radical prostatectomy group, 294 patients) and seven-year metastasis (combined radical prostatectomy and radiation therapy group, 438 patients).
The investigators found the following:
| Cox regression model results for prostate cancer metastasis using an AI algorithm | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Measure | NCCN risk categorization and VAI | NCCN risk categorization, PI-RADS, and VAI | NCCN risk categorization, radiologic T-stage, and VAI |
| Radiation therapy group | |||
| Adjusted hazard ratio (with 1 as reference) | 1.09 | 1.09 | 1.07 |
| Radical prostatectomy group | |||
| Adjusted hazard ratio (with 1 as reference) | 1.22 | 1.18 | 1.17 |
Yang and colleagues also reported that AUCs for seven-year metastases in the radiation therapy group for VAI and the NCCN risk category were 0.84 and 0.74, respectively, and that AUCs for five-year metastases in the radical prostatectomy group for VAI and the NCCN risk category were 0.89 and 0.79, respectively.
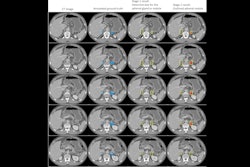
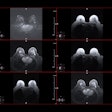
 AI-derived tumor volume at mpMRI and outcomes in localized prostate cancer. Image courtesy of Radiology.
AI-derived tumor volume at mpMRI and outcomes in localized prostate cancer. Image courtesy of Radiology.
The findings show promise for predicting prostate cancer treatment outcomes, but more investigation is needed, according to the authors.
"Further research involves extending this work to large multi-institutional data sets to better understand the prognostic information provided by the total volume of intraprostatic tumor from [AI]-generated segmentations," they concluded.
The complete study can be found here.