VIENNA - Adding digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) to digital mammography increased the breast cancer detection rate from 1.26% to 2.03%, in a study from Spain presented on Monday at ECR 2013.
The use of digital breast tomosynthesis has been on the rise for years, but how well does it work? That question is still being answered, especially as data emerge from clinical trials. Dr. Paula Martínez Miravete, from Clínica Universidad de Navarra in Pamplona, and colleagues sought to determine how much DBT improves breast cancer detection when combined with mammography, especially for American College of Radiology (ACR) density patterns 2, 3, and 4.
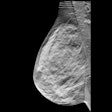
The study included 9,301 patients who received 2D digital mammography and tomosynthesis (Selenia Dimensions, Hologic) between December 2010 and September 2012. The patients had ACR density patterns of 2, 3, and 4.
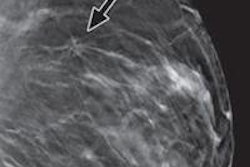
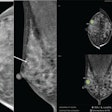
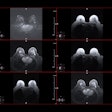
The researchers used two projections for conventional mammography and two projections for DBT. There were a total of 189 breast cancers; 118 tumors were detected via conventional digital mammography, for a detection rate of 1.26%.
"I'd like to mention this is an enriched population; we don't do screening," Martínez Miravete noted.
An additional 71 cancers not seen at mammography were detected using tomosynthesis: 14 in ACR 2 density, which increased the detection rate by 0.61%; 27 in ACR 3 (0.74%); and 30 in ACR 4 (0.87%).
No statistically significant differences were found in the detection rate among the three patterns, according to Martínez Miravete. Tomosynthesis increased the detection rate by 0.76%, so the total detection rate using the combination was 2.03%.
"There are no significant differences among the three ACR density patterns, so tomosynthesis can be useful not only in dense patterns but also in pattern 2," she said.
Two noteworthy points, Martínez Miravete added, are that the cancers were predominantly found in young women, and ACR 1 cases were excluded because the researchers didn't receive any new cases on tomosynthesis they hadn't seen before in conventional mammography.