A deep-learning model that combines CT radiomics and clinical information shows promise for predicting lymph node metastasis in bladder cancer patients, researchers have reported.
The study results could offer clinicians a better way to assess the prognosis of individuals with bladder cancer -- and thus tailor treatment, according to a team led by Rui Sun, PhD, of the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University in Shandong, China. The group's findings were published January 25 in Insights into Imaging.
"Lymph node metastasis affects the survival rate of bladder cancer patients … [and] because of the limitations of current diagnostic methods, there is an essential requirement for a noninvasive and precise method to predict [it] with bladder cancer," the team noted.
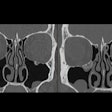
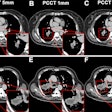
Conventional CT imaging hasn't proven significantly accurate to determine the lymph node status in individuals with bladder cancer, according to Sun and colleagues. They created a deep-learning radiomics model in an attempt to improve the modality's predictive ability.
The study included 239 patients who underwent three-phase CT imaging and resection for bladder cancers; of these, 185 were included in a training set for the model and 54 in an external test set. The team constructed the model using clinical characteristics and CT imaging features and identified the lesions' radiomics and deep-learning features. (The authors used the deep convolution network ResNet18 to extract deep-learning features for training and pretrained the model on the Onekey platform for transfer learning.) The model was presented as a nomogram, and the group assessed its performance using the area under the receiver operating curve (AUC) measure, accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value.
Overall, the team found that its combined deep learning model (CT radiomics plus clinical characteristics) showed higher accuracy, specificity, negative predictive value, and positive predictive value in the test set.
| Test set performance of 3 different models for predicting lymph node metastasis status in bladder cancer patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Measure | Clinical model | Radiomics alone | Combined model |
| AUC | 0.62 | 0.89 | 0.83 |
| Accuracy | 83% | 85% | 87% |
| Sensitivity | 30% | 40% | 40% |
| Specificity | 95% | 95% | 98% |
| Negative predictive value | 86% | 87% | 88% |
| Positive predictive value | 60% | 67% | 80% |
"Our proposed combined model using three-phase CT images is a noninvasive, readily available, and effective lymph node metastasis prediction tool for bladder cancer patients," the authors concluded. "We recommend its inclusion in bladder cancer predictive models for improved monitoring and adjuvant clinical trial design to narrow the gap between radiology and precision healthcare."
The complete study can be found here.