Thoracic manifestations of sickle cell disease.
Leong CS, Stark P
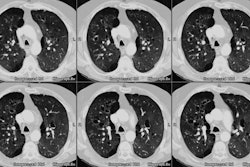
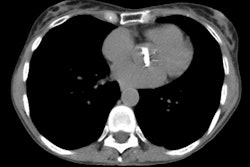
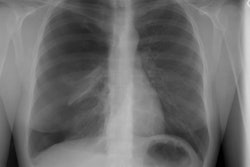
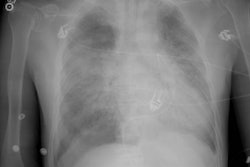
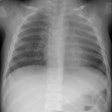
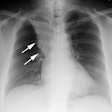
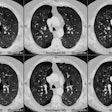
Sickle cell disease is the most common inherited disease in the African American population. Multiorgan pathologic features with a predilection for thoracic organs predominate. Acute cardiopulmonary diseases include acute chest syndrome, pneumonia, and left ventricular failure. Cardiomegaly, pleural effusions, pulmonary consolidation, pulmonary edema on chest radiographs, and ground-glass opacities on computed tomographs are characteristic. Chronic changes include sickle cell lung disease with lung fibrosis, pulmonary arterial hypertension, hyperkinetic circulation related to severe anemia, and thoracic skeletal abnormalities; the latter are H-shaped vertebrae, rib infarction, and extramedullary hematopoesis.
Publication Types:
Review
Review, tutorial