J Thorac Imaging 1995;10(1):43-57. Adult presentation of heterotaxic syndromes and related complexes.
Winer-Muram HT
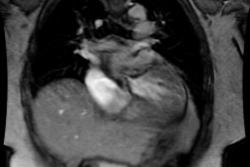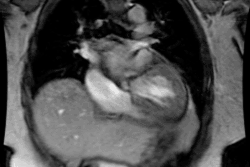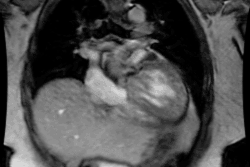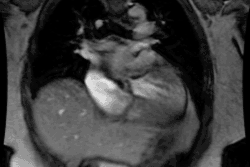
(Definitions) Situs solitus indicates the normal position of the cardiac atria and viscera. Situs solitus with levocardia is the normal situation, with < 1% incidence of congenital heart disease (Table 1). Levocardia denotes a left-sided heart and a left cardiac apex; it does not give any indication of cardiac structure or body situs (Fig. 1A). Situs inversus is the mirror-image location of the atria and abdominal viscera (Fig. 1B). Heterotaxia is the abnormal arrangement of organs and major blood vessels different from the orderly arrangement of either situs solitus or situs inversus. In situs ambiguus or heterotaxia, the relationship of the atria and viscera is inconsistent. Isomerism, a form of heterotaxia, is a term used to describe symmetric morphology, i.e., both sides of the viscera, and both lungs are nearly identical to one another (Fig. 2). Right isomerism or asplenia syndrome is characterized by situs ambiguus with bilateral right-sidedness (Fig. 2A). Left isomerism or polysplenia syndrome is a second type of situs ambiguus characterized by bilateral left-sidedness (Fig. 2B). In this review, all patients having situs ambiguus with either right isomerism (asplenia syndrome) or left isomerism (polysplenia syndrome) are regarded as having cardiac malposition, an inappropriate cardiac position.
PMID: 7891396, MUID: 95198352