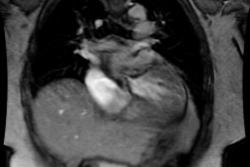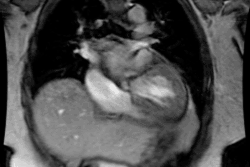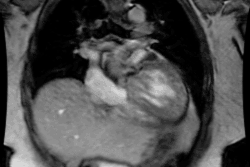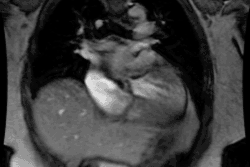
Congestive Heart Failure in the Neonate:
Clinical:
CHF in the neonate can be difficult to distinguish from pneumonia if the
heart is normal in size. Etiologies include: Large Endocardial Cushion
Defect; Arrhythmias; TAPVR with obstruction (Type 3), Cardiomyopathy: Viral-
Coxsackie Group B, Rubella or Glycogen Storage Disease (Pompe's); Coarctation
of the Aorta (Type I- infantile ); Endocardial fibroelastosis; Hypoplastic
Left Heart: Aortic Valvular Stenosis (Critical)/Atresia, Congenital Mitral
Stenosis, or Anomalous Left Coronary Artery (Left coronary artery arises
from the left pulmonary artery. Patients present about 6 months of age.
Retrograde flow will develop due to high systemic pressure); Peripheral
AVM: Vein of Galen aneurysm or Hemangioendothelioma; Congenital myocarditis;
Metabolic abnormalities: Hypoglycemia, Hypocalcemia, or Thyrotoxicosis;
and Cor Triatriatum.