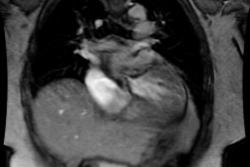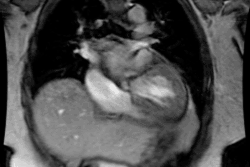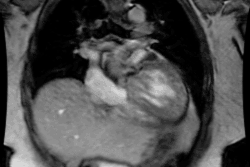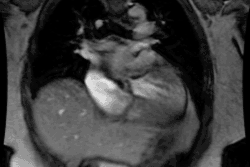
Pulmonary Sling (Aberrant Left Pulmonary Artery):
Clinical:
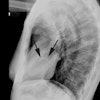
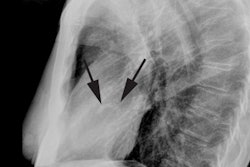
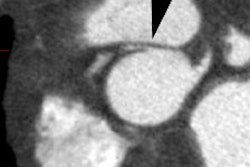
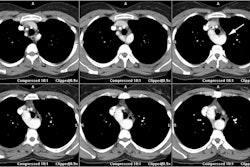
In this condition the left pulmonary artery is absent due to failure of development or obliteration of the pulmonary branch of the left 6th aortic arch. An aberrant left pulmonary artery then arises from the right pulmonary artery and runs posterior to the trachea (over the right mainstem bronchus) and anterior to the esophagus to get to the left lung. The pulmonary artery thus forms a sling around the distal trachea [2]. These patients commonly have associated tracheomalacia or tracheal stenosis which commonly leads to respiratory abnormalities even following correction of the vascular anomaly. Patients typically present during the neonatal period with respiratory symptoms such as stridor, apneic spells, and hypoxia [3]. Symptomatic patients are treated with surgical division and reimplantation of the anomalous left PA to the main PA [3].X-ray:
Plain x-ray may demonstrate obstructive emphysema or atelectasis of the right lung due to compression of the right mainstem bronchus [3]. On barium swallow there are posterior tracheal and anterior esophageal indentations due to the aberrant vessel.REFERENCES:
(1) Radiographics 2002; Zylak CF. Developmental lung anomalies in the adult: radiologic-pathologic correlation. 22: S25-S43
(2) Radiographics 2006; Castaner E, et al. Congenital and acquired pulmonary artery anomalies in the adult: radiologic overview. 26: 349-371
(3) Radiology 2008; Lee EY, et al. Multidetector CT evaluation of congenital lung abnormalities. 247: 632-648