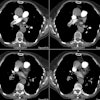
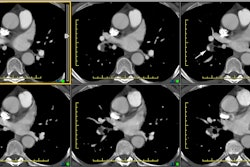
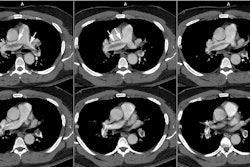
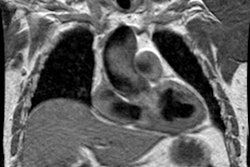
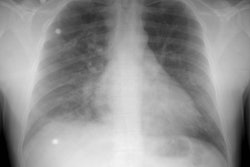
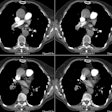
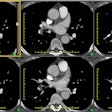
Radiology 1997 Aug;204(2):349-355. Intramural hematoma of the thoracic aorta: MR image findings and their prognostic implications.
Murray JG, Manisali M, Flamm SD, VanDyke CW, Lieber ML, Lytle BW, White RD
PURPOSE: To evaluate magnetic resonance (MR) imaging findings of intramural hematoma of the thoracic aorta and the irrelationship to prognosis. MATERIALS AND METHODS: MR images of 22 patients with intramural hematoma of the thoracic aorta were reviewed retrospectively. Site, thickness, degree of mural involvement, and signal intensity on spin-echo (SE) and cine gradient-echo (GRE) images of the hematoma were noted. MR findings of patients who did and those who did not develop complications were compared. RESULTS: Hematoma site was the only MR finding that correlated significantly with patient outcome. Complication frequencies in four (80%) of five patients with hematoma of the ascending aorta (type A) and in two (12%) of 17 patients with hematoma of the descending aorta (type B) were significantly different (P = .009). There were moderately strong correlations between days after symptom onset and signal intensity of the hematoma on SE (r = 0.78) and GRE (r = 0.72) images. MR images of two of three patients who developed early-subacute complications showed signal intensity changes of the hematoma that were consistent with recurrent bleeding. CONCLUSION: Patients with MR findings consistent with type A intramural hematoma of the thoracic aorta should undergo surgery. In cases of type B intramural hematoma of the thoracic aorta, MR imaging can be useful for detecting complete resolution or impending complications of the hematoma.
PMID: 9240519, MUID: 97382515